Entities Mapping
Mapping entities in SyncNow allows you to synchronize data between different work systems effectively. This process ensures that corresponding entities—such as bugs, stories, or tasks—are correctly aligned and kept in sync across systems.
📝 Step-by-Step Guide to Mapping Entities
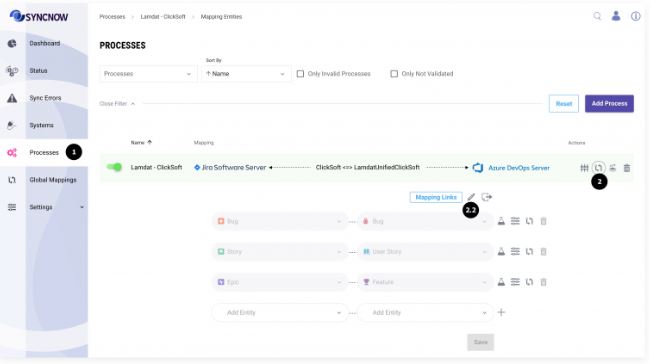
1️⃣ Navigate to the Processes Page
Go to the Processes page in the SyncNow application. This is where you will initiate the entity mapping process.
2️⃣ Initiate the Mapping Process
Press the Mapping Entities button.
If your process inherits a global mapping, press the Edit Global Mapping button to customize the inherited settings.
3️⃣ Select Entity Type Pairs
Identify and select the entity type pairs that need to be synchronized between the systems.
For example, you might map "Bug" in System A to "Bug" in System B, or "Story" in System A to "User Story" in System B.
This ensures that corresponding entities in different systems are correctly aligned for synchronization.
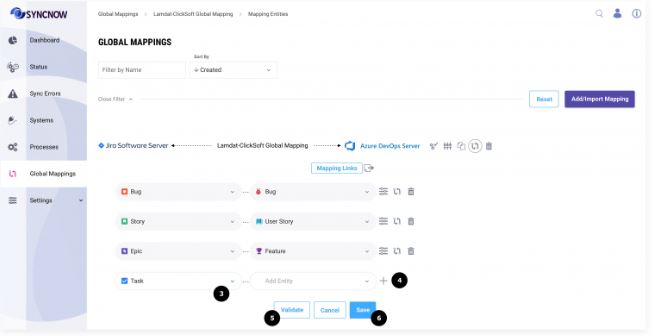
4️⃣ Add Additional Entity Pairs
If you need to map more entity pairs, press the Plus button to add additional pairs.
This allows you to extend the mapping to cover all necessary entity types across the systems.
5️⃣ Validate the Mapping
Press the Validate button to ensure that the new mappings do not disrupt any existing processes that have inherited the global mapping.
This validation step checks for conflicts and potential issues, ensuring the integrity of the synchronization setup.
6️⃣ Save the Mapping
After validation, press the Save button to finalize and save your entity mappings.
This commits the changes and makes the new mappings active for synchronization.
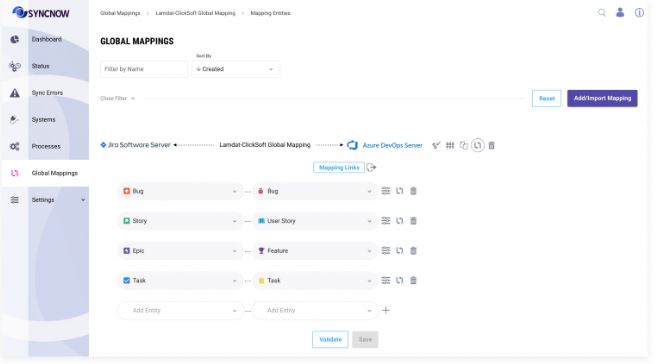
7️⃣ Confirmation of Mapping Creation
Once the entities mapping is created, you will see a confirmation message, and the new mappings will be listed in your configuration.
You can now proceed to configure additional mapping options if needed.
⚙️ Additional Configuration Options
After creating the entity mappings, you can further configure:
- Entity Mapping Options:
Define filters, logging options, conflict resolution settings, and whether to allow creation or restoration of entities on the target system. - Entity Links Mapping:
Configure how entities are linked or related between the systems. - Entity Fields Mapping:
Set up data transformations for each field to ensure proper synchronization. - Field Mapping Transformation:
Specify the direction of synchronization and any necessary transformations, such as picklist mapping, code snippet mapping, or pluggable mapping.
Tip:
Regularly review and validate your entity mappings to ensure smooth and accurate synchronization between your work systems.